Quaternionic Weber Local Descriptor of Color Images
Project summary:
Several local descriptors have been proposed using the Weber’s law (WL) that describes the ratio between the increment and initial intensity of a stimulus in the human visual system. WL is able to measure the local variation of the image contents in a relative manner. Numerous research results have shown that the derived descriptors are robust to different variations and show good discriminative abilities. However, for a color image, these types of descriptors are usually extracted from its grayscale version or from each color channel individually. They illustrate the local characteristics of the color image without considering the relations between color channels.
In this paper, a novel framework called Quaternionic Weber Local Descriptor (QWLD) is proposed for color image feature extraction. QWLD applies WL in the quaternionic domain such that the derived descriptors absorb both advantages of WL and QR. To show how to derive new descriptors using the QWLD framework, two descriptors, namely Quaternionic Increment Based Weber Descriptor (QIWD) and Quaternionic Distance Based Weber Descriptor (QDWD), are proposed as examples. They are based on different strategies to describe the increment and intensity of WL in the quaternionic domain.
Experiments are carried out to evaluate the proposed descriptors by different applications, and comparison results show their effectiveness.
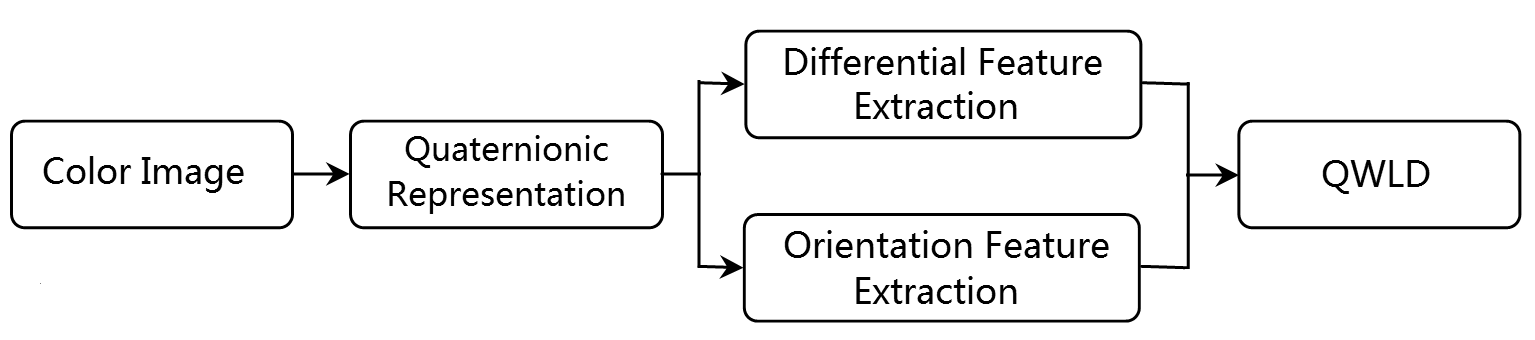 |
| Figure 1. The QWLD framework. |
Experimental results:
Table 1. RECOGNITION RESULTS ON TEXTURE DATA SET KTH-TIPS2-A USING DIFFERENT METHODS.
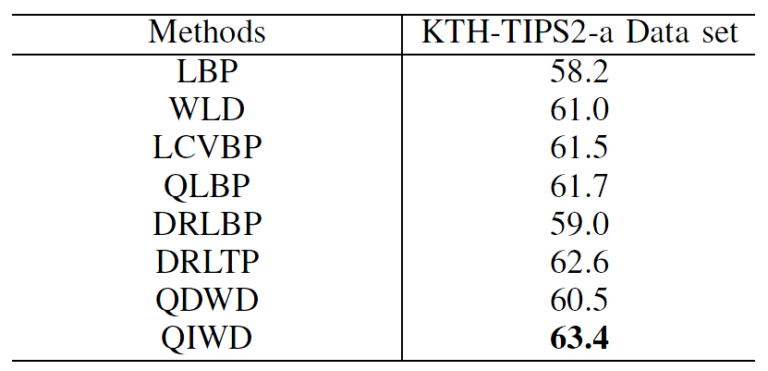 |
Reference:
Rushi Lan, Yicong Zhou*, and Yuan Yan Tang, “Quaternionic Weber Local Descriptor of Color Images,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, in press, 2016.